The plants in a green roof absorb water through their roots and then use surrounding heat from the air to evaporate the water while some roofs can reach temperatures of up to 90 f in the summertime these two features can allow green roofs to actually be cooler than the surrounding air temperature.
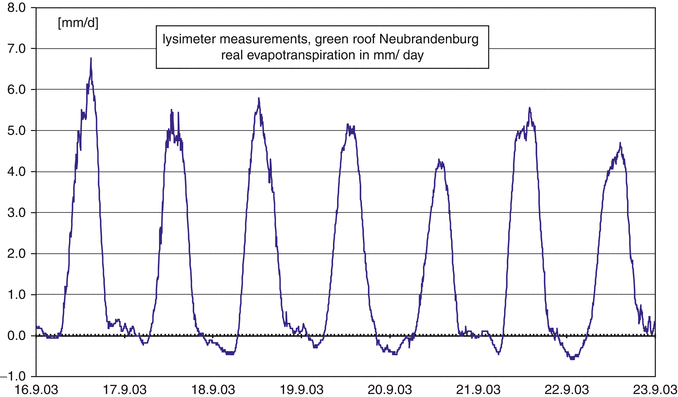
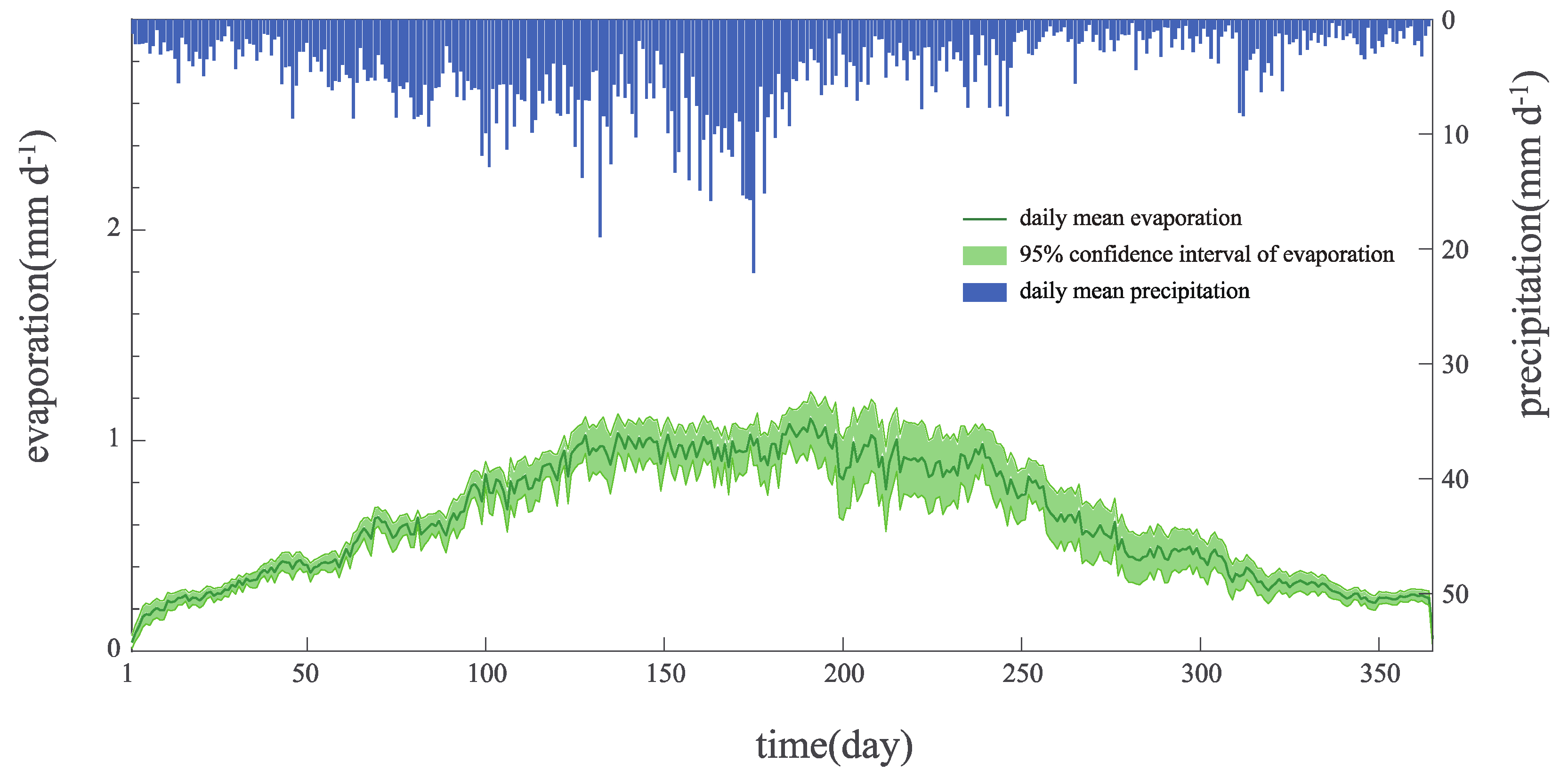
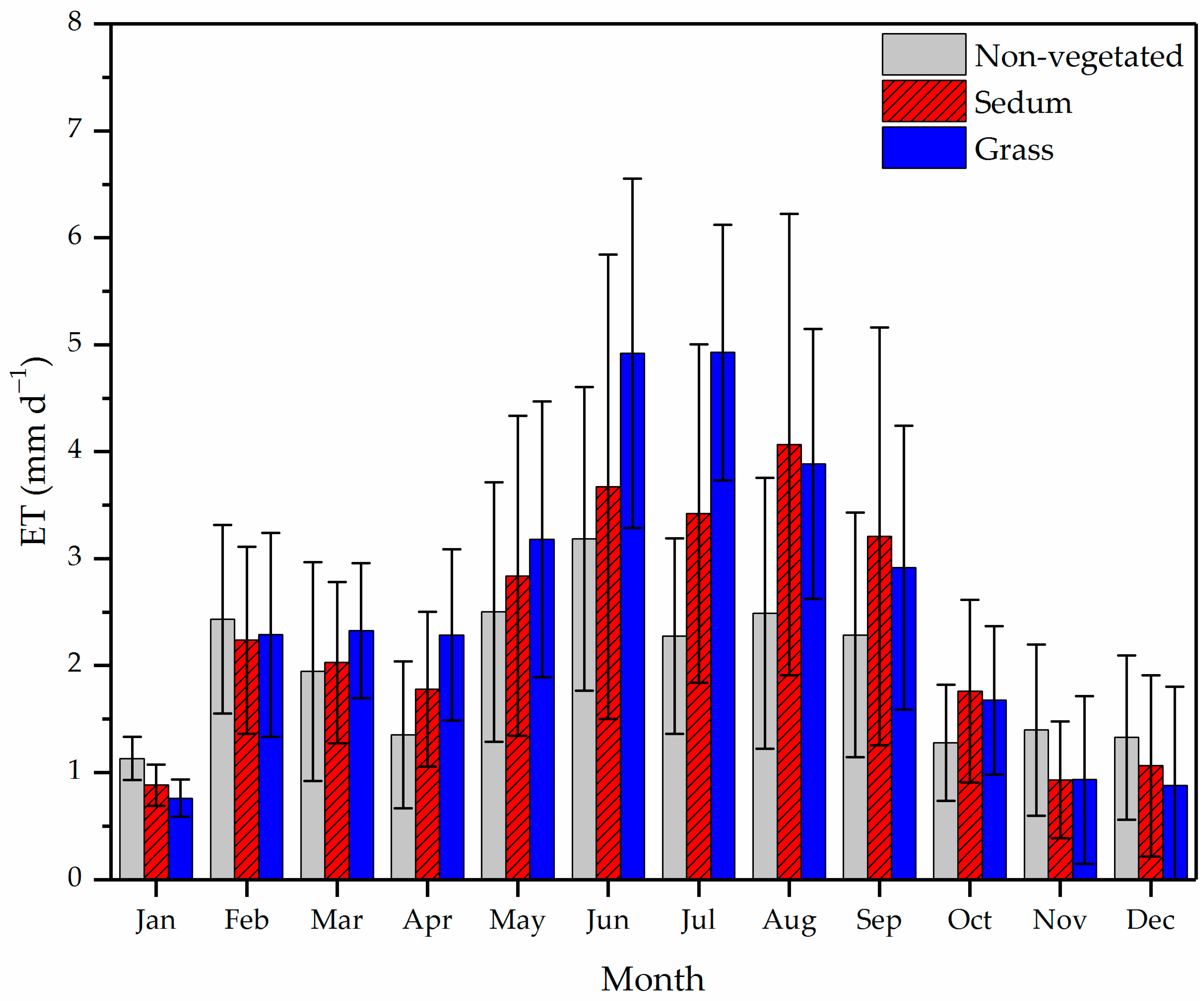
Green roof actual evapotranspiration.
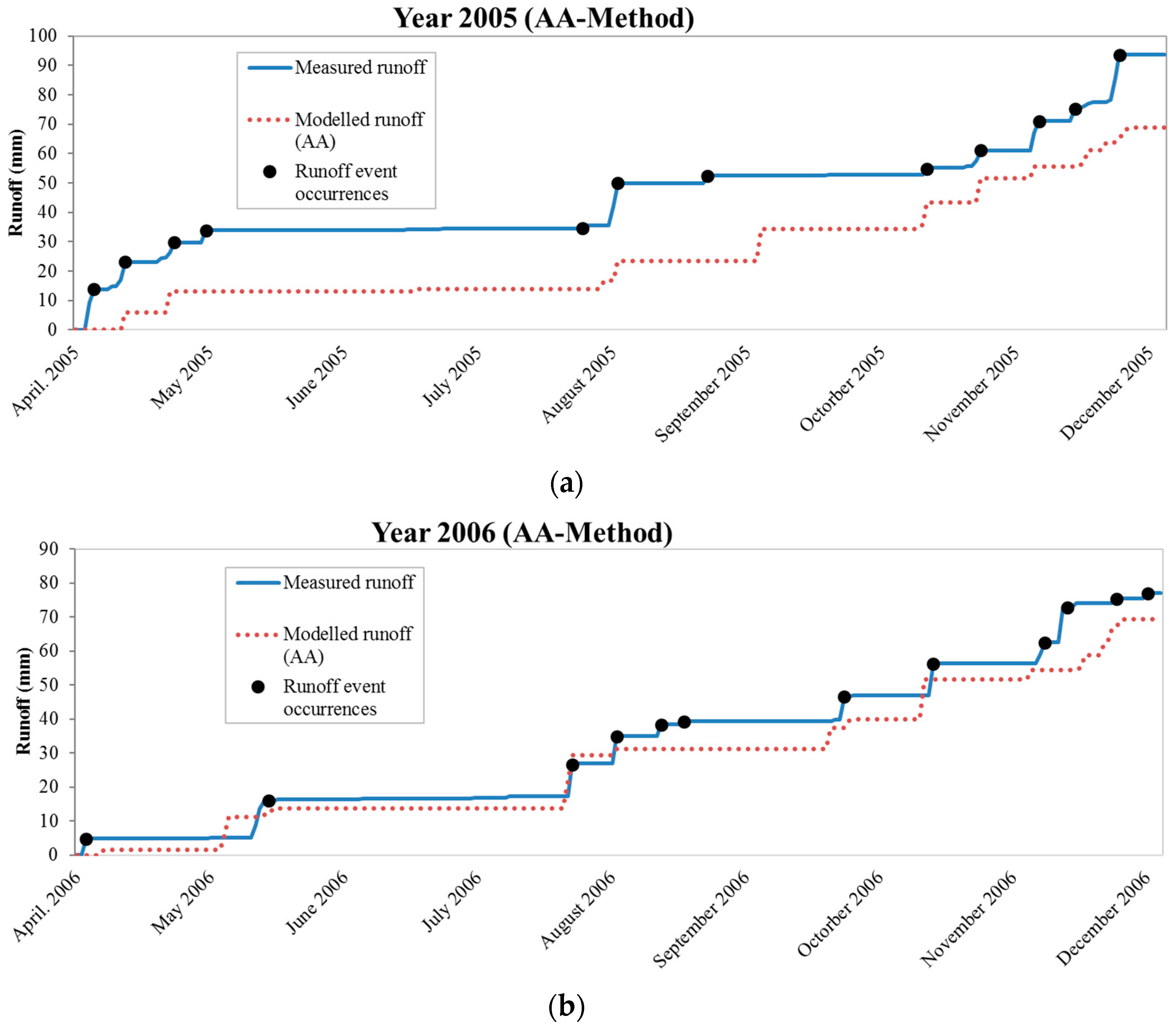
Green roof systems which calculate the runoff by solving the water balance equation account for precipitation irrigation storage and evapotranspiration processes rossman 2015.
Green roofs on campus.
If it s hot and windy the roof dries faster than if it s cool and still.
One truly cannot design a green roof without fully understanding the annual water balance and evapotranspiration rates of the plant palette in the making of green roof design.
Simpler equations have been applied to green roof such as the thornthwaite mather version neglecting the rooting depth and moisture stress or the soil moisture extraction function smef that further removes the restriction of wilting point 59 74 93 97.
Green roof is one of the emerging lid technologies used for retaining rainfall volume and attenuating storm runoff peak flows.
Course eco roof and green technologies.
After irrigation there was a substantial increase in latent heat flux for both green roof and bare soil.
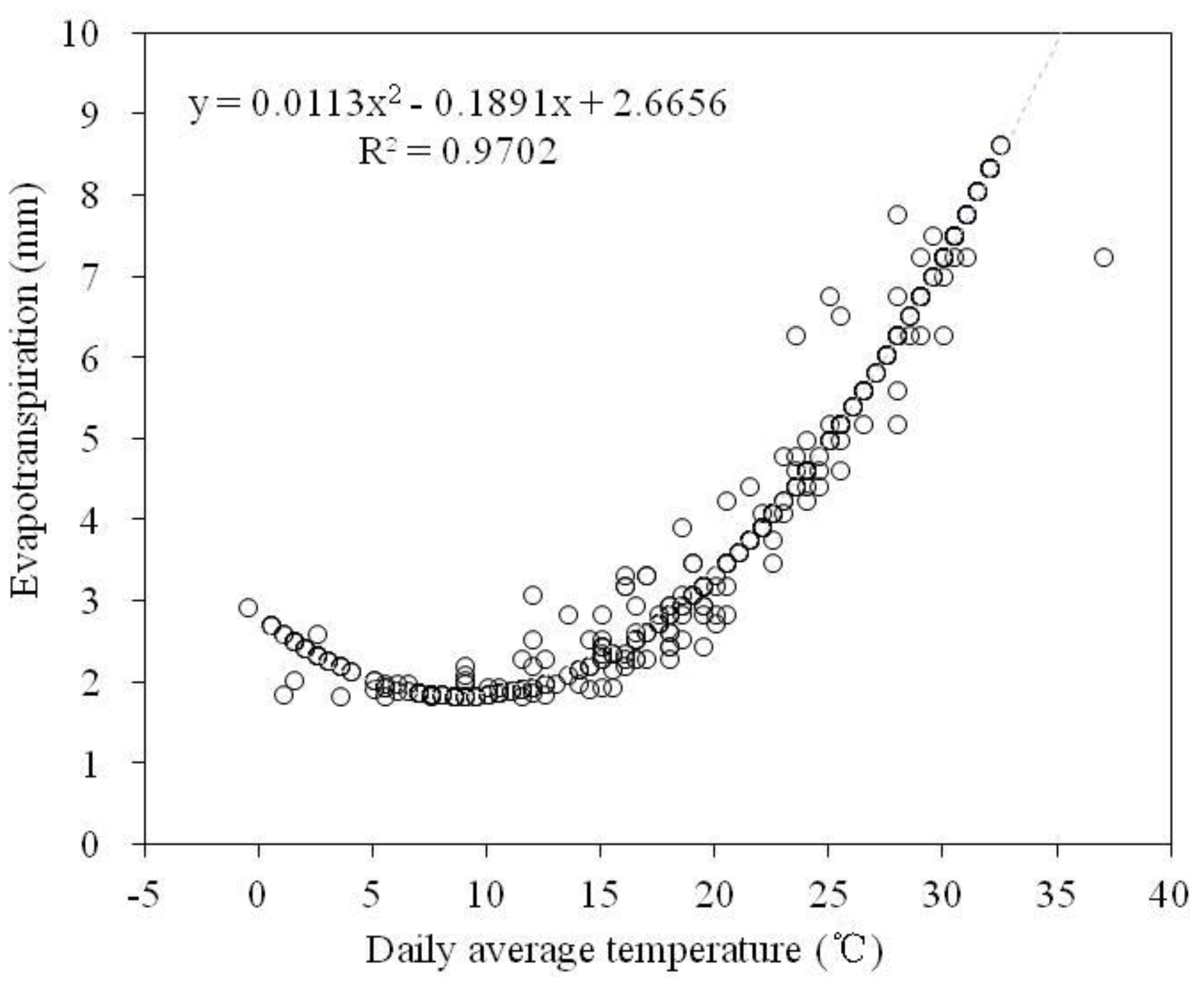
Actual evapotranspiration can be achieved by multiplying eto by ks.
Needless to say this is a task best left to the experts.
In the literature available however it is still not clear how and how much the evapotranspiration affects the performance of a green roof.
Considering that the sun can account for about 95 of the excess heat coming in through a roof evapotranspiration alone would lower the temperature of a typical extensive green roof by only a few degrees and leave us with a bunch of fried sedum.
2013 the higher latent heat flux on soil with maximum value about 280 w m 2 compared to green roof with maximum value about 210 w m 2 suggested that wet soil freely evaporated while evapotranspiration from the green roof was limited by the lower surface temperatures and water uptake by vegetation.
She pang 2010.
Evaporation is the loss of water from any old surface such as leaves and stems soil particles or debris.
Wind speed matters as it stirs up the so called boundary layer allowing water molecules to leave the surface as vapor.
On a green roof it s the same.
In coutts et al.
Evapotranspiration drives water requirements and hence irrigation scheduling and is the driver of retention.